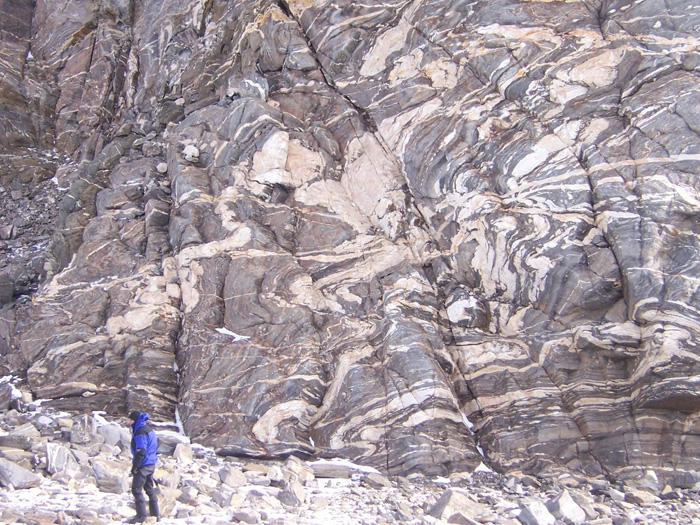
Since 1999, the rocks generally acknowledged to be the oldest on Earth were part of the Acasta gneisses in the Slave Craton in Canada’s Northwest Territories; specifically the Idiwhaa tonalitic gneisses. Zircons extracted from that unit yielded an age of 4.02 billion years (Ga) using U-Pb radimetric dating, revealing the time of their crystallisation from granitic magma. But nine years later some metabasaltic rocks from the tiny (20 km2) Nuvvuagittuq Greenstone Belt on the eastern shore of Hudson Bay were dated using the Sm-Nd method at almost 4.3 Ga (see: At last, 4.0 Ga barrier broken; November 2008). Taken at face value the metabasaltic rocks seemed to be well within the Hadean Eon (4.6 to 4.0 Ga) and could thus represent primary crust of that antiquity. However, U-Pb dating of zircons from thin sodium-rich granitic rocks (trondhjemites) that intrude them yielded ages no older than about 3.8 Ga. Similar ages emerged from zircons found in metasediments interleaved in the dominant mafic unit. Discrepancies between the two completely different dating methods resulted in the Hadean antiquity of the mafic rocks having been disputed since 2008. It was possible that the Sm-Nd results from the metabasalts may have resulted from the original mafic magmas having inherited a Hadean Sm-Nd isotopic ‘signature’ from their mantle source. That is, they may have been contaminated and could have formed in the early Archaean.

Jonathan O’Neil, now at Ottawa University in Canada, led the first isotopic investigation of the Nuvvuagittuq Greenstone Belt and has engaged in research there ever since. Further field and laboratory studies revealed that the previously dated mafic rocks had been intruded by large, chemically differentiated gabbro sills. A team of geochemists from the University of Ottawa and Carleton University, including O’Neil, has now published isotopic evidence from the intrusions that suggests a Hadean age for their parent magma (C. Sole et al. 2025. Evidence for Hadean mafic intrusions in the Nuvvuagittuq Greenstone Belt, Canada. Science, v. 388, p. 1431-1435. DOI: 10.1126/science.ads8461). The authors used the decay schemes of two radioactive samarium isotopes 147Sm and 146Sm; a significant advance in radiometric dating. The first decays to 143Nd with a half-life of about 1011 years, the second to 142Nd with a much shorter half life of about 108 years. Due to its more rapid decay, in geological terms,146Sm is now much rarer than 147Sm. Consequently, using the short-lived 146Sm-142Nd decay system is technically more difficult than that of the 147Sm-143Nd system. But the team managed to get good results from both the ‘fast’ and the ‘slow’ decay schemes. They tally nicely, yielding ages of 4157 and 4196 Ma. The gabbros provide a minimum age for the metabasalts that they cut through. The original 4.3 Ga Sm-Nd date for the metabasalts is thus plausible. Sole and colleagues consider the dominant metabasaltic rocks to have formed a primary crust in late Hadean times that was invaded by later mantle-derived mafic magma about 100 Ma later. The granitic rocks that constitute about one third of the Nuvvuagittuq terrain seem to have been generated by partial melting more than 300 Ma later still, during the Palaeoarchaean.
Perhaps similar techniques will now be deployed in granite-greenstone terrains in other cratons. Many of the older ones, generally designated as Palaeoarchaean in age, also contain abundant metamorphosed mafic and ultramafic igneous rocks. Perhaps their origin was akin to those of Nuvvuagittuq; i.e. more Hadean crust may await unmasking. Meanwhile, there seems to be more to discover from Nuvvuagittuq. For instance, some of the rocks suggested to be metasediments interleaved in the metabasalts show intricate banding that resembles products of bacterial mat accumulation in younger terrains. Signs of Hadean life?
Since the first reliable radiometric dating of Archaean rocks in 1971, there has been an element of competition to date the oldest rocks on Earth: to push history back towards the initial formation of the Earth. It is one of the most disputatious branches of Earth history. Rivalry may play a significant part in driving the science, as well as the development of novel dating techniques and the continuing discovery of clearly old relationships using ‘old-fashioned’ relative dating, such as signs of intrusion, unconformities etcetera. But in some cases there is a darker side: the potential for profit. Recently, samples from Nuvvuagittuq appeared for sale on the Internet, priced at $10,000. They may have been collected under the guise of supplying museums by a group that shipped-in mechanical excavators in 2016. Unsurprisingly this angered the local Innuit community of Inukjuak. They were also worried about bona fide collection for scientific research that had left parts of the small, once pristine area somewhat battered, including cultural features such as an inukshuk navigational monument. Their fury at commercial exploitation of their homeland resulted in the community council closing the area to collecting in 2024. I emphasise that this violation of basic geological ethics was by commercial rock collectors and dealers, not academic geologists. The local people are now considering careful issue of research permits so that important research can continue. But further rock collecting may remain banned.
See also: New Research Verifies Northern Canada Hosts Earth’s Oldest Rocks. Scienmag, 26 June 2025; Gramling, C. 2025. Earth’s oldest rocks may be at least 4.16 billion years old. ScienceNews.
PS With many thanks to ‘Piso Mojado’ for alerting me to this paper