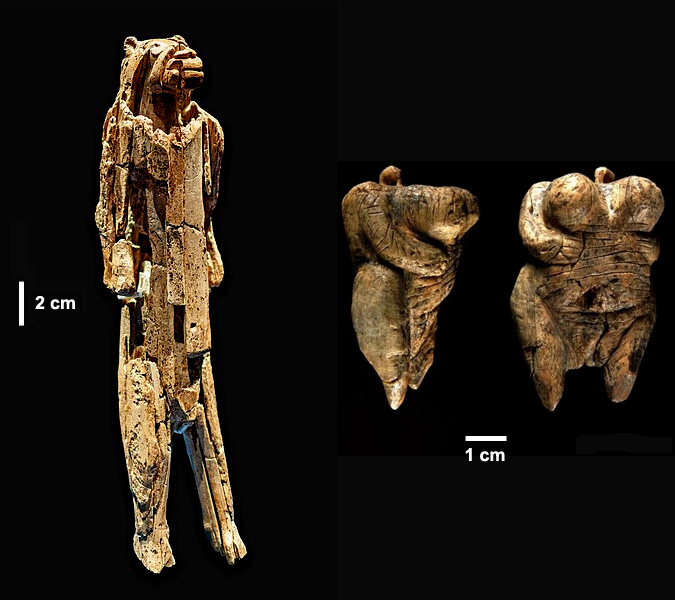
The colours of human skin, eyes and hair in living people across the world are determined by variants of genes (alleles) found at the same place on a chromosome. Since chromosomes are inherited from both mother and father, an individual may have the same two alleles (homozygous), or one of each (heterozygous). A dominant allele is always expressed, even if a single copy is present. A recessive allele is only expressed if the individual inherits two copies of it. Most characteristics of individuals result from the interaction of multiple genes, rather than a single gene. A commonly cited example is the coloration of eyes. If we had a single gene for eye colour – that of the iris – that had alleles just for blue (recessive or ‘b’) and one for brown (dominant or ‘B) pigmentation, brown-eyed individuals would have one or two ‘B’ alleles (bB or BB), whereas those with blue eyes would have to have two ‘blue’ alleles (bb). But inheritance is more complicated than that: there are people with green, hazel or grey eyes and even left- and right eyes of different colour. Such examples suggest that there are more than two genes affecting human eye colour, and each must have evolved as a result of mutations. Much the same goes for hair and skin coloration.
A group of scientists from the University of Ferrara in Italy have analysed highly detailed ancient DNA in anatomically modern human remains from Russia (Palaeolithic), Sweden (Mesolithic) and Croatia (Neolithic) to tease out the complexities of pigmentation inheritance. Then they applied a statistical approach learned from that study to predict the likely skin-, eye- and hair pigmentation in 348 less detailed genomes of ancient individuals whose remains date back to 45 Ma ( Silvia Perretti et al, 2025. Inference of human pigmentation from ancient DNA by genotype likelihood. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, v. 122, article e2502158122; DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2502158122).

All the hunter-gatherer Palaeolithic individuals (12 samples between 45 and 13 ka old) bar one, showed clear signs of dark pigmentation in skin, eyes and hair – the outlier from Russia was probably lighter. Those from the Mesolithic (14 to 4 ka) showed that 11 out of 35 had a light eye colour (Northern Europe, France, and Serbia), but most retained the dark skin and hair expected in descendants of migrants from Africa. Only one 12 ka hunter-gatherer from Sweden had inferred blue eyes, blonde hair, and light skin. The retention of dark pigmentation by European hunter-gatherers who migrated there from Africa has been noted before, using DNA from Mesolithic human remains and in one case from birch resin chewed by a Mesolithic woman. This called into question the hypothesis that high levels of melatonin in skin, which protects indigenous people in Africa from cancers, would result in their producing insufficient vitamin D for good health. That notion supposed that out-of-Africa migrants would quickly evolve paler skin coloration at higher latitudes. It is now known that diets rich in meat, nuts and fungi – staple for hunter-gatherers – provide sufficient vitamin-D for health at high latitudes. A more recent hypothesis is that pale skins may have evolved only after the widespread Neolithic adoption of farming when people came to rely on a diet dominated by cereals that are a poor source of vitamin-D.
However, 132 Neolithic farmers (10 to 4 ka ago) individuals studied by Perretti et al. showed increased diversity in pigmentation, with more frequent light skin tones, yet dark individuals persisted, particularly in southern and eastern Europe. Hair and eye colour showed considerable variability, the earliest sign of red hair showing up in Turkey. Even Copper- and Bronze Age samples ( 113 from 7 to 3 ka) and those from Iron Age Europeans (25 from 3 to 1.7 ka ago) still indicate common retention of dark skin, eyes and hair, although the proportion of lighter pigmentation increased in some regions of Europe. Other analyses of ancient DNA have shown that the Palaeo- and Mesolithic populations of Europe were quickly outnumbered by influx of early farmers, probably from the Anatolian region of modern Turkey, during the Neolithic. The farming lifestyle seems likely to have allowed the numbers of those who practised it to rise beyond the natural environment’s ‘carrying capacity’ for hunter-gatherers. The former inhabitants of Europe may simply have been genetically absorbed within the growing population of farmers. Much the same absorption of earlier groups seems to have happened with the westward migration from the Ukrainian and Russia steppes of the Yamnaya people and culture, culminating in the start of the European Bronze Age that reached western Europe around 2.1 ka, The Yamnaya introduced metal culture, horse-drawn wheeled vehicles and possibly Indo-European language.
So the novel probabilistic approach to ancient DNA by Perretti et al. also casts doubt on the diet-based evolution of light pigmentation at high latitudes. Instead, pulses of large population movements and thus changes in European population genetics probably account for the persistence of abundant evidence for dark pigmentation throughout Europe until historic times. The ‘lightening’ of Europeans’ physiognomy seems to have been vastly more complex than previously believed. Early Europe seems to have been almost bewilderingly diverse, which make a complete mockery of modern chauvinism and racism. The present European genetic ‘melting pot’ is surprisingly similar to that of Europe’s ancient past.